Have you been concerned about business practices in Indonesia and how you search for land?
In particular, the number of companies expanding into Indonesia, which has a huge market that drives the ASEAN economy, is increasing, but the procedures for land acquisition are unclear, as regulations regarding the type of real estate ownership by foreigners change every few years. It is very confusing.
For those in charge of projects considering construction plans in Indonesia, we provide assistance in purchasing land for factories and warehouses near Jakarta, Indonesia, and research on industrial parks. We have summarized the flow and precautions.
This article was created by Plus PM Consultant Sdn. Bhd., a construction consultant based in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, who provides project management and construction management to support companies expanding into the ASEAN region.
Overview of construction land acquisition in Indonesia and Land ownership
Can foreigners purchase the land?
Land ownership is the right of individuals who own Indonesian nationality, and foreigners cannot purchase land due to Indonesian policy.
Business rights and construction rights can be held by Indonesian citizens or by corporations established under Indonesian law and headquartered in Indonesia.
Usage rights (Hak Pakai) are granted to Indonesian citizens and legal entities established under Indonesian law that are headquartered in Indonesia, as well as foreigners residing in Indonesia and foreign companies with representative offices in Indonesia.
HGU:Hak Guna Usaha
Rights for agriculture, fisheries, and livestock. In principle, it is allowed for a maximum of 25 years, with the possibility of extension for a further 25 years. If a company or business requires it for a long period of time, HGU for up to 35 years may be granted. However, the right will be applied in industrial area only, the right will be different from non-industrial area.
HGB:Hak Guna Bangunan
Right to construct and own a building on land. The right to construct and own a building on unowned land for up to 30 years. It can be extended for up to 20 years.
However, the right will be applied in industrial area only, the right will be different from non-industrial area.
HP: Hak Pakai
The right to use and harvest the products in the land under direct control of the State or owned by a person who has been granted rights and obligations as determined by a competent authority or in a land use contract, unless inconsistent with the spirit and provisions of the law.。Others: usage rights, land lease rights, cultivation rights, forest product collection rights
Therefore, foreigners can establish a local corporation and use the above rights to use land in Indonesia for a specified period of time.
What kind of land should I choose?
The best method for selecting construction sites for foreign companies is to ”purchase a plot in an area suitable for construction use from a developer who operates an industrial park.”
Why an industrial park?
In Indonesia, it is difficult to carry out redevelopment projects within existing cities or to construct new projects by clearing mountain forests for the following reasons;
- In redevelopment projects, land acquisition may be difficult because the rights are complicated and the authenticity of the title is unclear, such as the content of the title being different from the actual title.
- Land development projects require connections with the government and landowners, knowledge of real estate development, and local experts who can handle the work.
- The Indonesian government restricts the construction of manufacturing facilities to industrial parks.
Therefore, in general, foreign companies often select land within industrial parks that have been developed through development discussions with the government.
Industrial park near Jakarta
Industrial parks are operated by major conglomerates alone or jointly with major Japanese trading companies.
Development permits are obtained based on the national comprehensive plan, and land uses, regulations, and rights are clearly defined in advance between the government and the developer. In the suburbs of Jakarta, Japanese trading companies are involved in the management of industrial parks such as MM2100, DELTAMAS (GIIC), KIIC, and SURYACIPTA, while locally owned ones include LIPPO CIKARANG and JABABEKA.
Photo: MM2100 INDUSTRIAL TOWN

*Quoted from Material of Industrial Park, BKPM
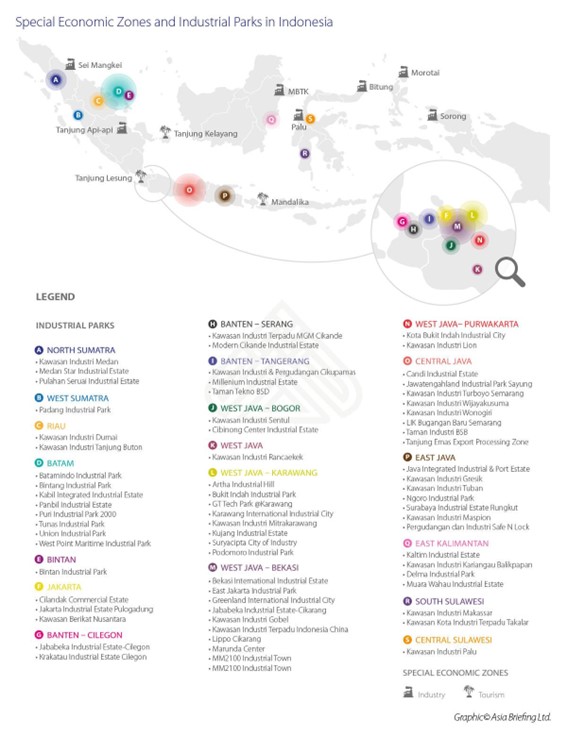
Reference:https://www.wowshack.com/fascinating-map-of-special-economics-zones-and-industrial-parks-in-indonesia/
Flow of land acquisition procedures
We explained earlier that industrial parks receive development permits based on the national comprehensive plan, but since the government issues business permits to each area individually, the flow of land acquisition and construction varies depends on industrial park.
Therefore, when selecting land, it is necessary to understand the characteristics of each industrial park, confirm whether the facility concept is feasible, and compare construction sites based on operational regulations.
The general flow of land acquisition methods and land acquisition procedures in Indonesia is as follows;
| STEP1 | Property selection (confirmation of evaluation criteria) |
| STEP2 | Tour the property and check with the land office |
| STEP3 | Examination of related documents |
| STEP4 | Confirmation of property delivery conditions such as price and conditions with seller |
| STEP5 | Confirmation of land title by land deed preparation officer |
| STEP6 | Payment of income tax and name change fee |
| STEP7 | Creation of land transfer deed – Payment of land cost (usually 3 to 5 installments) – Signing of the deed (The sale is completed when both parties sign the land transfer deed only after the payment is confirmed) – Change of name on title deed |
| STEP8 | Obtaining HGB |
Key points when selecting a construction site
1) When selecting land: Confirm the surrounding environment and infrastructure that will affect the facility layout plan
To avoid problems during the design and construction stages, it is necessary to check the following: If you do not check the requirements here, the project will be interrupted in the worst case, so please be careful.
- Surrounding environment
- Rivers, ponds, marshes, and cadastral records before construction
- Differences of heights
- Infrastructure (electricity, gas, water and sewage, industrial wastewater facilities, etc.)
- Green areas, urban planning regulations, and setbacks
- Building coverage ratio, floor area ratio, height restrictions, etc.
- Legal requirements
2) After land selection: Construction land acquisition and construction flow
After selecting the land, you can obtain the right to build (HGB) by making a purchase reservation, paying an advance payment, checking the land title by a land deed preparation officer, signing a land sales contract, paying the land fee, and then preparing a real estate transfer deed.
In addition, as a characteristic flow of the construction application procedure in Indonesia, once the land fee payment is completed, it becomes possible to apply for a building permit (PBG) and an environmental application (UKL/UPL or AMDAL), and then the construction work procedure begins, then apply SLF after construction is done.
3) Points to note when registering
Indonesia also has a registration system, but unlike Japan, it is not open to the public, so disclosure is required from the registered rights holder.
Land registers are created and managed by the competent land bureau. Furthermore, in rural areas, it is not uncommon for there to be a large amount of unregistered land called “adat.”Generally, the period required for registration is relatively long, and there is a large amount of unregistered land, especially in suburban and rural areas, so it is necessary to carefully investigate land rights.
Real estate appraiser
Real estate appraiser is a national qualification recognized by the Ministry of Finance (Kementerian Keuangan).
Appraisal standards are established by the Indonesian Association of Professional Appraisers (MAPPI: Masyarakat Profesi Penilai Indonesia), and appraisals are conducted using the appraisal standard SPI (Standar Penilaian Indonesia).
Indonesia has a strong awareness of globalization, and has been proactive in creating the Indonesian Valuation Standard (SPI) by referring to the International Valuation Standards (IVS) from an early stage.
However, the Indonesian land system has a deep-rooted local custom called adat, so it is important to check the appraisal standards.
Real estate defects
In Indonesia, there is no obligation to explain important matters stipulated by Japanese law (an explanation that real estate brokers are required to provide before signing a contract when buying, selling, or intermediating land or buildings).
It is the buyer’s responsibility to inspect the condition of the property they are purchasing to determine if there are any defects in the property.
Even if the buyer has a legal right to claim or terminate the contract on the basis of any defects found in the property after the contract has been concluded, it may be extremely difficult to enforce such claims.
Taxes and costs on land acquisition
| Taxes and costs | Percentage |
| Land/building acquisition tax (income tax/name change fee) | 5% |
| Buying and selling land deeds | 1% |
| Lawyer’s fee | 0.50%~1.50% |
| Registration fees (including administrative fees and stamp duty) | 0.20% |
| Fixed asset tax | 0.1~0.3% |
| Real estate agent fees * Generally, the seller pays. * Either the buyer or the seller pays, but it cannot be both. | 5% |
Industrial parks in Indonesia
Below is the list of industrial parks in Indonesia

Reference: https://www.asean.or.jp/ja/invest/country_info/indonesia/industrialestate/ , ASEAN-JAPAN CENTRE
Conclusion
- Land ownership is the right of individuals who own Indonesian nationality, and foreigners cannot purchase land.
- Foreigners establish a local corporation and use Indonesian land for a specified period of time, usually by using construction rights.
- Recommend purchasing plots in areas suitable for construction purposes from developers who operate industrial parks.
- When selecting land, it is important to check the surrounding environment and infrastructure that will affect the facility layout plan.
- Since it will be extremely difficult to pursue liability for defects against the seller after the contract has been signed, the business owner should proactively eliminate the risk.
For those who are considering investment in Indonesia
Plus PM Consultant Sdn. Bhd. has experience working on projects in Jakarta, Indonesia and will be able to check on the due process of the permitting procedures by checking and monitoring design for compliance and monitor the submission process to each authorities, as per the sequence.
Plus PM Consultant has also collaborated with experienced local Permitting Consultant, Designers and Project Management companies on projects in Indonesia.
Furthermore, Plus PM being a Japanese company has access to latest information from Japanese business community, chamber of trade & industry and embassy.

This article is produced by Plus PM Consultant Sdn. Bhd. based on Indonesia’s local information obtained through news coverage, as well as the links and references stated below.
We go to great length to ensure that the informational contents on this website and article are as accurate as possible. However, the accuracy of the contents of the article is not always guaranteed. Unauthorized reproduction of these contents is not allowed
≫Citation, references, bibliography